Medical device design and development is an extremely complex, multi-phase process. A crucial aspect of it is biocompatibility testing to ensure that the materials used in the medical device are safe for patient use. There are various types of biocompatibility tests, and they are largely dependent upon the specifications of the medical device. In this article, we discuss various aspects of biocompatibility testing for medical devices in detail.
What is Biocompatibility Testing for Medical Devices?
Biocompatibility testing for medical devices is a critical and extensive process that ensures that the medical devices are safe for their intended use. Biocompatibility testing also ensures that when a medical device comes in direct or indirect contact with the human body, it does not produce any type of adverse biological response or effects such as irritation, inflammation, or toxicity.
When Do Medical Devices Need Biocompatibility Testing?
Biocompatibility testing isn’t required for all medical devices. It is, however, required for almost all medical devices that come in contact with human tissue, either through direct or indirect contact. Let’s understand the difference between these two types of contact:
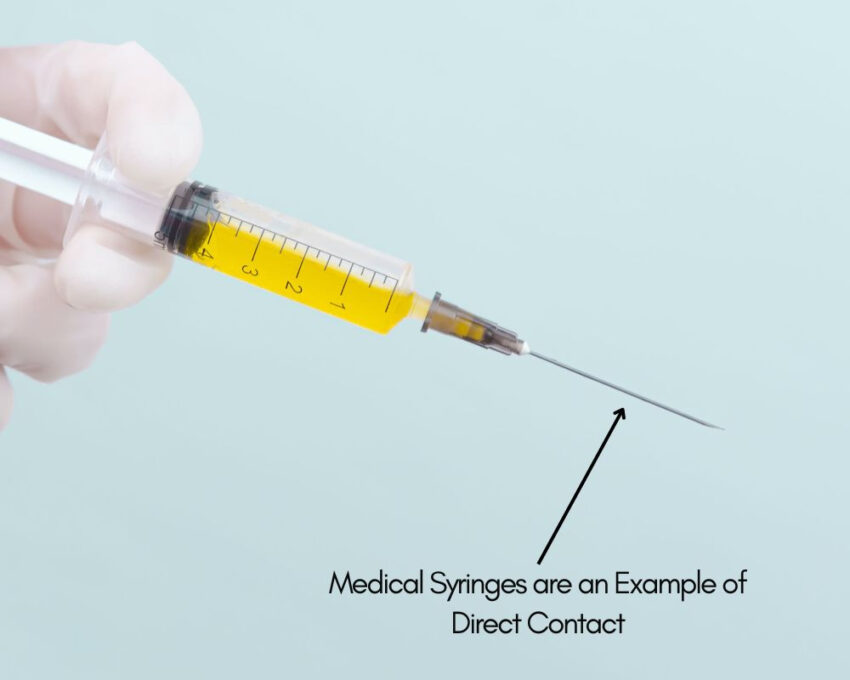
- Direct contact is when the medical device or the components of the medical device come in physical contact with tissues of the human body.
- Indirect contact is when any type of fluid or gas first passes through the medical device or the components of a medical device, after which it comes in contact with the tissues of the human body.
To summarize, all medical devices that are either in permanent or prolonged contact with the body are required to undergo biocompatibility testing. This also applies to all medical devices that are in indirect contact, even if it’s for a brief period.
If the medical device is an external device that does not come in any form of contact with the body tissues, then biocompatibility testing may not be required. For instance, Medical devices such as wound dressings, stents, surgical instruments, and catheters are required to undergo extensive biocompatibility testing, whereas non-contact diagnostic devices such as X-rays and ultrasound scanners are not required to undergo biocompatibility testing.
Types of Biocompatibility Testing
There are various types of biocompatibility tests. Let’s understand some of the key types of biocompatibility tests for medical devices:

Cytotoxicity Testing
Cytotoxicity testing refers to testing toxicity toward biological cells. It is typically required when medical devices come in direct contact with the body tissues. E.g., implants, catheters, dental materials, etc.
Cytotoxicity testing determines whether the materials affect cell health. Cytotoxicity testing ensures that the materials of the device do not release any type of toxic or harmful substances that could cause damage to the cells and tissues.
The guidance document for cytotoxicity testing is as per ISO 10993-5 standards.
Sensitization Testing
Sensitization tests are carried out to evaluate whether the materials of the medical device can cause sensitizations or allergic reactions in patients. These tests enable manufacturers to identify whether materials in medical devices can trigger immune responses. Sensitization testing can be performed using either the material or specific chemicals from the material.
Sensitization testing is typically performed for medical devices that come into contact with skin or eyes. E.g., contact lenses, wearable monitors, etc.
The guidance document for sensitization testing is as per ISO 10993-10 standards.
Irritation Testing
Irritation testing analyzes whether the materials of the medical device irritate the skin, eyes, or mucous membranes. These types of tests determine any type of discomfort or damage to the tissue at the contact site. Irritation testing is especially necessary for medical devices that come in contact with sensitive and injured areas. E.g., wound dressings, surgical gloves, bandages with adhesives, etc.
The guidance document for irritation testing is as per ISO 10993-23 standards.
Systemic Toxicity
Systemic toxicity analyzes the toxic effects of material leachables when the medical device enters the body. This type of testing is carried out if there is systemic exposure. It assesses the risk of the medical device or its materials that can cause harmful effects throughout the body. Let’s understand the various types of systemic toxicity tests:
- Acute systemic toxicity evaluates the effects of short-term exposure, i.e., within 24 hours to the materials of the medical device.
- Subacute toxicity identifies potential toxicity from prolonged but non-chronic use. It evaluates the effects of repeated exposure for 14 to 28 days.
- Subchronic toxicity identifies the delayed toxic effects of the medical device materials. It evaluates the effects of repeated exposure of over 28 to 90 days.
- Chronic toxicity identifies potential risks of long-term exposure to the medical device materials. It evaluates the effects of toxicity over 90 days to several months or years.
The guidance document for systemic toxicity testing is as per ISO 10993-11 standards.
Pyrogen Testing
Pyrogens are substances that can induce fever or inflammation upon entering the bloodstream or if they come in contact with the tissue. Pyrogen testing ensures the safety of blood-contacting devices, injectable devices, and implantable materials. The guidance document for pyrogen testing is as per ISO 10993-11 standards.
Genotoxicity Testing
Genotoxicity testing analyzes whether the materials of the medical device can cause genetic damage when they come in contact with the human body. It is an extremely crucial aspect of biocompatibility testing for medical devices that incorporates a set of in vitro and in vivo tests to detect mutagens. The guidance document for genotoxicity testing is as per ISO 10993-3 standards.
Reproductive And Developmental Toxicity
Reproductive and developmental toxicity testing evaluates the potential effects of the material device and its materials on fertility, reproductive health, and fetal development. They are required for devices that are implanted and in contact with reproductive organs. The guidance document for reproductive and developmental toxicity is as per ISO 10993-3 standards.
Implantation Tests
Implantation tests determine the biocompatibility of medical devices when they come in direct contact with living tissue other than the skin. They are performed to assess the local tissue response and material degradation and are applied to evaluate both absorbable and non-absorbable materials. The guidance document for implantation tests is as per ISO 10993-6 standards.
Hemocompatibility Testing
Hemocompatibility tests analyze the interaction of the medical device with blood. Another type is the hemocompatibility analysis is required for all medical devices that can come into direct or indirect contact with blood as it determines the extent of damage that the materials of the medical device can cause to the red blood cells.
Hemocompatibility tests ensure that the medical device does not cause any type of adverse effects, such as clot formation or red blood cell damage. The guidance document for hemocompatibility tests is as per ISO 10993-4 standards.
How Biocompatibility Testing for Healthcare Products Works
Biological Evaluation Plan (BEP) Development
The very first step of biocompatibility testing is to start by creating a biological evaluation plan.
BEP, abbreviated for Biological Evaluation Plan, considers the entire biological risk profile of the medical device. It reviews the entire medical device, its components and materials, and suggests all possible evaluations and testing to address risks.
BEP outlines the testing strategy of the medical device based on its intended use, potential toxicological threats, contact time, and type with the body. BEP ensures that all safety considerations and regulatory requirements are met.
Evaluation and Testing
In the next stage, biocompatibility tests that are identified in the BEP are carried out. This typically combines various types of tests that range from chemical analysis, in vivo or in vitro biological tests, toxicological risk assessment, and clinical evaluations to ensure patient safety.
In Vitro and/or In Vivo Testing
Those tests assess the interaction of medical devices and their materials with the human body and its systems.
In vitro tests are performed in test tubes or petri dishes using animal cell cultures and tissues, whereas in vivo tests are performed on animals.
Clinical Evaluation
In most cases, clinical evaluations are required for certain high-risk devices, and it involves testing the medical device in a clinical setting. Clinical evaluations help manufacturers gather performance data and validate patient safety.
Chemical Analysis of Materials
This step involves chemical analysis of all the materials that are used in the medical device. In addition to the chemical characterization, this step also identifies potential contaminants that can affect biocompatibility.
Toxicological Risk Assessment
A toxicological risk assessment evaluates the potential harmful effects of the medical device and its materials on the body.
Toxicological risk assessment makes use of data from the chemical analysis of materials and biological testing to identify and mitigate risks, thereby ensuring patient safety for medical devices.
Review & Documentation
Finally, the last stage is to review all the data from the performed biocompatibility tests and document the findings in a comprehensive report. This report is referred to as the Biological Evaluation Report, abbreviated as BER.
BER illustrates that the medical devices meet all the relevant biocompatibility requirements and is further submitted as supporting documentation for regulatory approval. BER, along with all the test results, are submitted for a conformity assessment to approve the medical device.
Regulatory Requirements of Biocompatibility Testing for Medical Devices
ISO Requirements: ISO 10993 – Part 1
The main guidance document that outlines the essential requirements for biocompatibility testing for medical devices is ISO 10993 – Biological evaluation of medical devices.
Many medical devices are required to undergo biocompatibility testing as per the ISO 10993 standard. The scope of biocompatibility testing depends upon the medical device, contact type, and duration, and the parameters of biocompatibility testing for medical devices are set forth by ISO 10993 – Part 1.
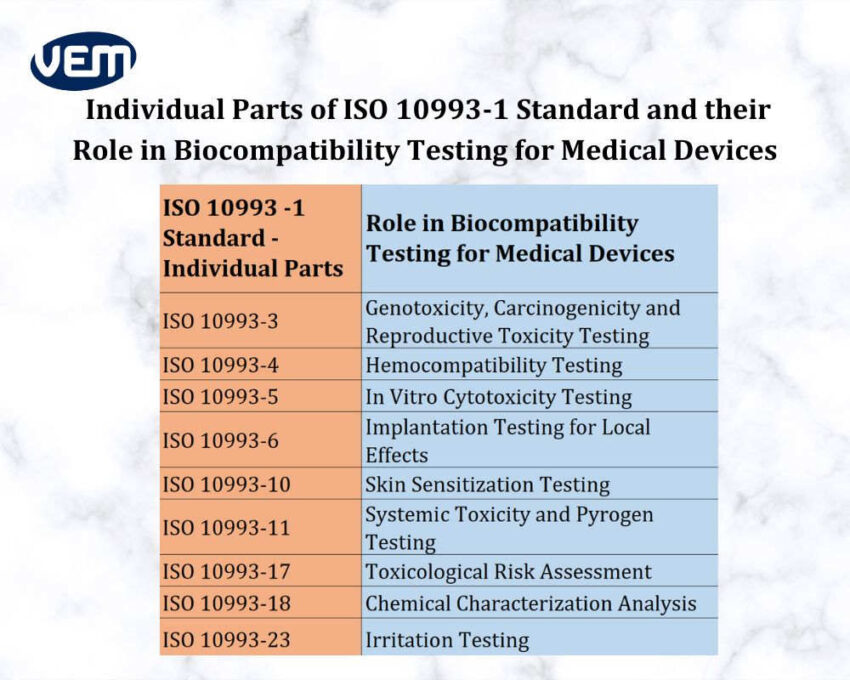
Part 1 of the ISO 10993 standard enlists the information and guidance for conducting biocompatibility testing for medical devices. Within the ISO 10993 standards, there are various parts of biocompatibility testing standards, and the following parts of ISO 10993 describe the assessment for individual biocompatibility testing properties. The following infographic illustrates the individual parts of the ISO 10993 standard and their role in biocompatibility testing for medical devices:
You can read more about ISO 10993 Part 1 here.
FDA Requirements
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) emphasizes a risk-based approach to selecting appropriate tests for biocompatibility evaluation of medical devices.
FDA emphasizes integrating biocompatibility evaluation within a risk management process throughout the medical device’s lifecycle. This approach ensures that potential biological risks by the medical device materials are identified, assessed, and mitigated effectively. The FDA provides comprehensive guidance on biocompatibility testing for medical devices, explained by International Standard ISO 10993-1. This guidance document, developed by the FDA, is referred to as FDA’s Biocompatibility Guidance on Use of ISO 10993-1. It outlines the framework for assessing the potential biological responses of the medical device’s interaction with the human body.
FDA’s biocompatibility assessment resource center also explains the concepts and terms that are necessary for medical device biocompatibility requirements. Medical device manufacturers must consider the FDA’s guidance documents and ISO 10993-1 standards. This is to ensure that the biocompatibility evaluations align with the requirements of the regulatory agencies. An additional benefit is a smoother premarket submission process.
European Union Medical Device Regulation (EU MDR) Requirements
All medical device manufacturers seeking to market their devices in the European market have to ensure their devices are biocompatible.
The EU MDR requires a comprehensive assessment of the biocompatibility of the medical device for market approval. It aligns with the ISO 10993 standards and includes the biocompatibility evaluation as part of the technical documentation. This ensures that the medical device meets all relevant safety and performance criteria.
EU MDR takes ISO 10933-1 as a standard to provide relevant guidelines and information on the products to be biocompatible. You can read more about the EU MDR here.
Contact Us
Biocompatibility testing is a crucial aspect as it ensures that the medical devices are safe for patient use and in compliance with regulatory agencies.
VEM Medical has over 20 years of experience in manufacturing high-quality medical devices. We understand the importance of regulatory compliance in the medical device industry and can guide you in developing a robust risk management process that incorporates biocompatibility testing for your medical device.