

The manufacturing of medical devices is a complex process and one of the most challenging aspects of this process is attaching the parts together safely and permanently. Poor bonding within the medical device isn’t acceptable as it can lead to catastrophic failures that can endanger both the patient as well as the medical professional.
Irrespective of the medical device application, the bonding process should be perfect! Correct bonding within the medical equipment is imperative for the reliability of the device and patient safety. In this article, we discuss various fundamentals of the assemblies and how they impact the performance of any medical device.
Medical device assembly is the process of assembling any type of medical device in a clean manufacturing environment. This includes taking manufactured parts or components of devices and combining them to build a finished product. Medical device assembly is applied to a wide range of devices, all the way from syringes, insulin pumps, stethoscopes, and wheelchairs to magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) parts and surgical equipment.
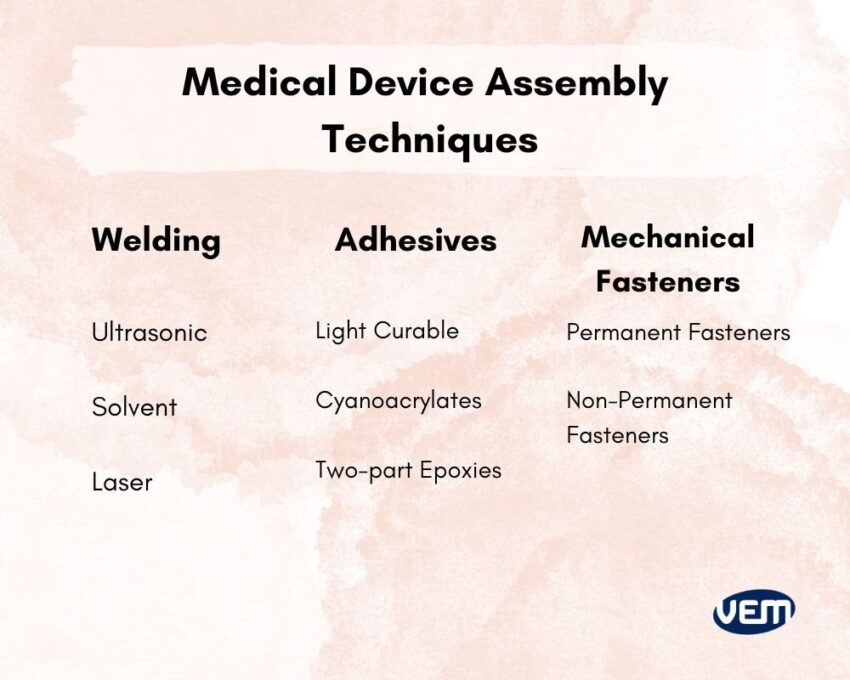
In medical device assembly, various types of techniques and materials are implemented to connect the components and subcomponents together. It is imperative to use the right type of technique and material. This is largely dependent upon the type of medical device and its specifications.
For instance: Co-Dx PCR Kits have many parts and sub-components and they are assembled together with specialized materials in cleanrooms. These materials are used as per the regulations and product quality standards.
The assembly of medical devices must be carried out in cleanrooms as it requires contamination-free environments. They also need extensive attention to detail and thus, calibration equipment and automated assembly systems are necessary and validated by the FDA to enforce such tight tolerances. In addition, there are various regulations that govern the assembly of medical devices such as the environment must be sterile and special air filters must be incorporated to remove contaminants from air.
Today, assembly technologies of medical devices have evolved to achieve flexibility and scale production but they must adhere to various compliance and regulatory requirements. In order to discover the most efficient assembly process, it is important to understand the product’s purpose. You should note that the functions of medical devices vary considerably thus, some devices can be assembled more easily than others. Complex medical devices need complicated equipment and tools. We have listed below some of the services that are common in medical device assembly:
Manual assembly can be carried out for both, simple or complex parts that have numerous components. They are usually considered for small-batch orders.
Semi-automated assembly is considered when the batch numbers are relatively higher and manual assembly is no longer cost-effective. This type of assembly offers greater efficiency as well.
If the quantity is high, then fully automated assembly processes are an optimum choice. Fully automated assembly processes can be designed for simple as well as complex products.
There are some core requirements to qualify as a medical device assembler. Let’s take a look at these requirements:

A medical device assembler must be well-versed with respect to clean room environment protocols. In addition, they should be able to operate high-speed automated machinery in a clean-room environment and know how to use tools and chemicals that are necessary to install required materials in medical devices. They should adhere to protocols such that they are able to maintain clean rooms in a way that there is no scope for contamination of medical products.
A medical device assembler must be able to develop dexterity in order to deliver high-quality medical devices. They should be able to perform various operations with respect to assembly, sub-assembly, and packaging in the operations area efficiently.
It is crucial to ensure that the quality standards are not just followed according to the product standards but they are also in accordance with the compliance set by the regulatory bodies. A medical device assembler must follow all production processes in order to maintain product quality standards and they should adhere to the ISO standards and federal regulations.
They must be able to read, understand, and implement manufacturing procedures so that they can assemble medical devices correctly. In addition, they should also be able to inspect medical devices thoroughly in a clean room facility to ensure that the quality standards are met.
There can be no scope for error when designing medical devices and equipment. It is crucial to undertake a holistic view of the medical device during the design phase, which should include the assembly stage. In order to ensure that the assembled medical device is as per the product quality standards, design engineers must consider the following factors:
It is imperative to consider the assembly process in the early design phase itself, as an incorrect technique can damage the part. You should also note that the parts cannot undergo assembly right after molding as they need to cool completely, otherwise, it can lead to defects such as warping. It is thus critical to include the assembly technique in the design phase as it creates a more streamlined approach that prevents part fragility.
Since medical devices have tight tolerances, the assembly technique must be aligned with the production such that the design parameters aren’t altered. If the assembly technique is not correct, then the design can be compromised. Thus, it is critical to consider tight tolerances, when designing for medical devices.
Medical devices are heavily regulated and operators must follow strict protocols and adhere to the regulations. Special parameters may include instances such as needles or bodily fluid tubes that need to be sterile are often ‘no touch’ products. It is thus important to consider such parameters early on in the design phase.
Mechanical fasteners are often the minutest components in a medical device but they are responsible for not just the assembly but holding the entire unit together. If a mechanical fastener fails in a medical device, then there is a high chance that the medical device will also fail. It is thus, pressing that the fastener is aptly installed.
Fasteners mechanically join two or more parts together. There are various types of fasteners and they are distinct from each other with respect to functionality. Fasteners are broadly categorized into permanent or non-permanent fasteners. Permanent fasteners such as rivets and nails form a permanent joint between the parts whereas the non-permanent fasteners form a temporary joint and are designed for easy removal and re-use. Let’s take a look at some of the most common mechanical fasteners:
One of the techniques that is applied to assemble medical devices effectively is plastic welding. Medical device welding is a distinct expertise where the part sensitivity towards heat and distortion varies considerably from other industries. In the case of medical devices, the thin walls require precise welding. You should also note that medical devices have tight tolerances and thus, it is imperative that welding in medical devices is conducted accurately.
In this section, we discuss three important plastic welding technologies i.e. ultrasonic, solvent, and laser welding. Let’s understand these techniques further:
Ultrasonic welding makes use of high-frequency vibrations to assemble the parts. This is achieved through a vibrating tool that is commonly referred to as a horn or sonotrode. Along with the vibrating tool, ultrasonic vibrations are created with the help of various components such as the power supply, converter, and booster. These components deliver mechanical vibration to the parts and the heat generated between the parts bonds them together.
Ultrasonic weld cycles are extremely fast, and thus, this technology is widely used for production runs that have high-volumes. Some of the examples of ultrasonically welded products with respect to medical devices are catheters, cannulas, and trocars.
You should note that various types of thermoplastics such as polystyrene and nylon, can be welded ultrasonically. It is ideal if both the plastics are of the same material but different plastics can also be bonded via ultrasonic welding if their melting temperatures are similar.
There are various medical device applications such as implantable medical sensors and analyzers, where ultrasonic welding may not be the fit due to the vibrations. In such cases, laser welding proves to be an excellent alternative.
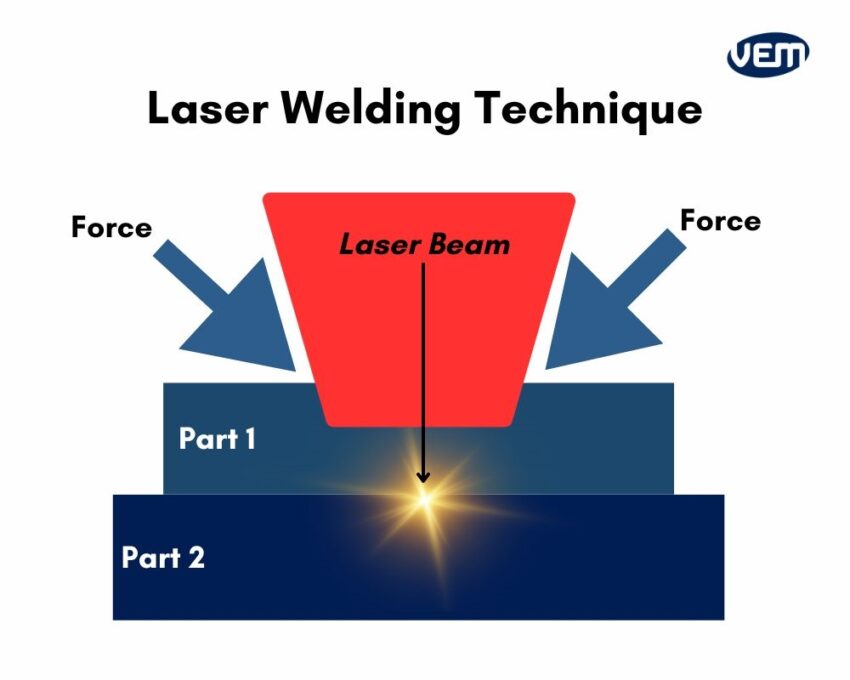
The near infrared heat created in laser welding bonds the parts together and this is provided by a light source. Laser welding equipment consists of a stand that includes one or more laser light sources, or diodes. These light sources are typically in the range of 780–980 nm and they are delivered to the parts through fiber optic bundles. These bundles are arranged around the part perimeter which creates configurable weld zones. The following image demonstrates laser welding:
The solvent welding technique is a type of welding technique that makes use of solvents to bond the plastic parts together. Solvent welding is relatively inexpensive and it creates durable, hermetic bonds that are at most minimally visible.
Solvent welding is widely applied to assemble joints and manufacture hermetic seals in medical devices.
There are various types of adhesives that are applied to assemble medical devices and the correct adhesive for the application is based on the design of the medical device. These adhesives are used for gap filling, high-strength bonding and sealing, and easy in-line processing. Some of the most common adhesives that are applied for assembling medical devices are light-curable adhesives, cyanoacrylates, and two-part epoxies. Let’s understand these adhesives further:
Light-curable adhesives cure quickly when exposed to the right wavelength and intensity of light. They almost cure immediately, within as little as 2 seconds. Once cured, these adhesives can achieve a rigid state or remain soft and flexible. This is largely dependent upon the formulation.
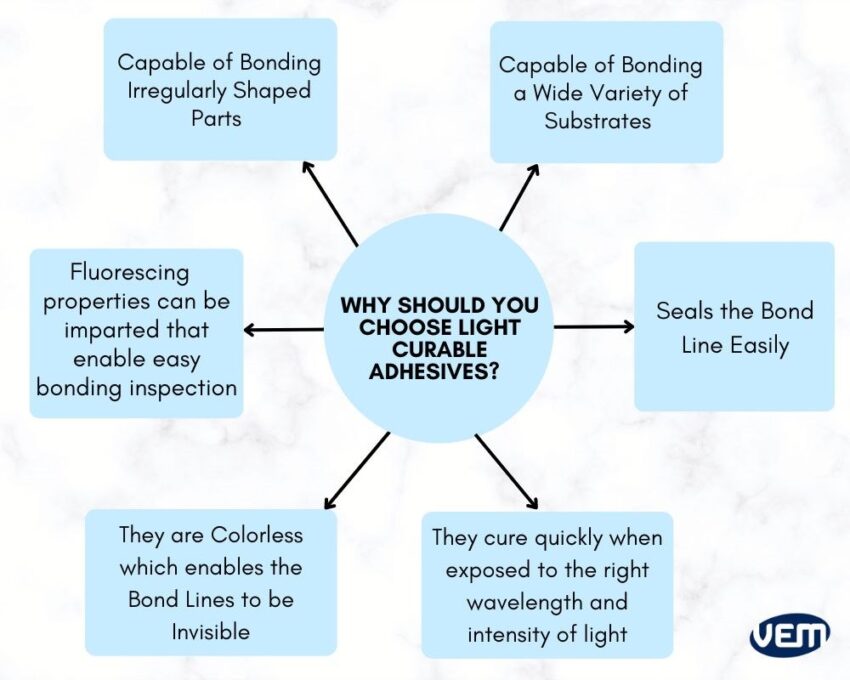
Light-curable adhesives pose significant advantages such as they can be formulated with fluorescing properties that enable easy inspections of the bonding and they are also available with an array of properties thus, they can be applied to various assembly applications. In addition, they demonstrate excellent thermal and chemical resistance that enables the medical devices to be subjected to sterilization processes.
Cyanoacrylates cure within 10-60 seconds and in the presence of moisture. They demonstrate high shear strength and cure quickly but they are also very brittle, have low impact resistance, and are subject to stress cracking, which often leads to bond failures.
Two-part epoxies comprise a resin and a hardener, which must be mixed before dispensing. They demonstrate excellent chemical resistance but they are very rigid and have low impact resistance.
There are several assembly techniques that can be used to adhere parts of medical devices together. These techniques range all the way from mechanical to bonding types and each of these techniques pose certain challenges. Let’s understand these challenges further:
Mechanical fasteners, though effective, pose high levels of stress and strain on the assemblies. This is because bolted assemblies and rivets require a hole which is not suitable for smaller or delicate devices thus, they can be used only for larger and heavy-weight assemblies that can handle the high-stress and strain of mechanical fasteners.
Adhesives are extremely popular and they offer distinct advantages over other bonding processes. They can eliminate joint fatigue, distribute load, and improve impact resistance. They do, however, require setting and curing time but generally, adhesive bonding is more efficient than other techniques.
In ultrasonic welding, plastic substrates are held together by applying pressure, which enables the parts to fuse together. This technique is extremely effective however; at times, there may be gaps due to bond gap variances.
In the case of solvent welding, plastic parts are coated with a solvent and pressed until the solvent evaporates thus, letting the parts fuse together. The challenge with this process is that there is a high risk of the plastic cracking due to stress.
Medical device assembly is a specialized process that requires the right tools, equipment, and experience. If it’s not done correctly, the bonding will not be apt leading to failed assemblies of the medical device.
At VEM-Medical, we have design experts and engineers who can help you choose the right assembly technique for your project! Our team has vast experience and they focus on streamlining the production and the assembly process. If you have any questions with respect to medical device assembly or manufacturing, you can contact us and we will get back to you right away!