

A core aspect of medical device manufacturing is maintaining compliance with regulatory bodies to ensure quality and safety. A lack of regulatory compliance can lead to infractions, warnings, and revoking of licenses.
Medical professionals and patients expect that their medical devices are of high quality, efficient, and safe to use. Government regulators ensure that the end-user demand is met consistently which makes quality regulations for medical device manufacturers a priority! Complying with the requirements of the various regulatory bodies and the ongoing evolution of the regulatory agencies requires organization, standardization, and vigilance. Medical device manufacturers thus deploy quality management systems to meet regulatory standards.
In this article, we explain the medical device quality management system, its purpose, some of the regulations governing the QMS, and how it can help to solve the regulatory quagmire for medical device manufacturers.
Medical Device Quality Management System, abbreviated as QMS is an integral aspect of quality management.
Quality management in general, aims to meet or exceed customer requirements. However; in the medical device industry, quality management is necessary for regulatory compliance and market access. Medical device manufacturers must comply with the various regulations to ensure that the medical devices meet the set standards.
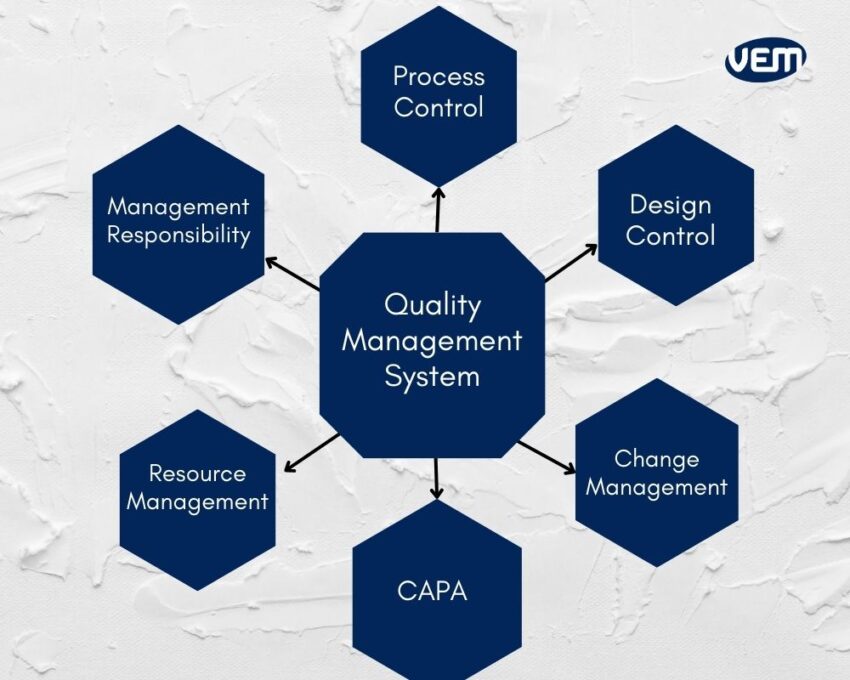
The main objective of QMS is to manage the quality and efficiency of the medical device through a set of implemented policies, and procedures. A medical device QMS is a structured system that enlists the various processes and procedures implemented throughout the product life cycle of a medical device.
The purpose of a medical device QMS is to ensure that the medical device is safe and effective for its intended use. A medical device QMS includes all aspects of design and development, manufacturing, risk management, clinical data, storage, distribution, and product labeling.
Medical device manufacturers are required to implement and maintain a QMS that is compliant with the various international and national regulations and guidelines.
The complexity of the QMS largely depends upon the medical device classification. Medical devices of Class II (medium-risk) or Class III (high-risk devices) will require a different QMS implementation than medical devices of Class I (low-risk). Thus, it is critical to understand the medical device classification before building a QMS.
You should note that quality management systems can be paper-based or electronic.

A paper-based QMS typically would include physical documents in binders and signed paper copies that are scanned and stored. These can be accessed through an internal network.
This type of system is cost-effective and easy to implement. However; it’s not a very convenient option for a large and complex organization as these paper-based QMS systems are more prone to human error.
An electronic QMS, or eQMS, consists of procedures and templates in the form of electronic documents. These documents are distributed, reviewed, and approved electronically. It’s an end-to-end electronic process that’s often faster and more efficient. This system also reduces the risk of errors significantly, but its implementation requires a significant investment.
An effective eQMS solution streamlines quality processes, controls, and management documents to achieve compliance.
Medical device manufacturers can manage their QMS with the correct resources that can handle manual paperwork. However; regulatory requirements are forever evolving and its complexity makes managing quality processes manually a challenging and daunting task.
Today, various medical device manufacturers are migrating to eQMS solutions and cloud-based document storage to improve their workflows and reduce time.
The ideal stage for building a medical device QMS is when your team has gathered enough information and knowledge. This is typically around the design and development phase.
You should note that timing is a critical aspect when building a QMS thus, it is not advisable to delay it for long. It is recommended that you start the development of QMS during the early prototype phase.
The development of medical device QMS is dependent upon various factors such as the complexity and classification of the device, its intended markets, and regulatory approvals.
It typically takes approximately 3 to 9 months to establish a complete medical device QMS. You should note that a document template for processes and protocols helps to speed up the implementation.
Complying with the regulatory agencies is typically the driving force for developing a QMS however; you should note that the QMS is not simply a set of procedures that must be followed for an inspection. A QMS helps to manufacture high-quality and efficient devices consistently.
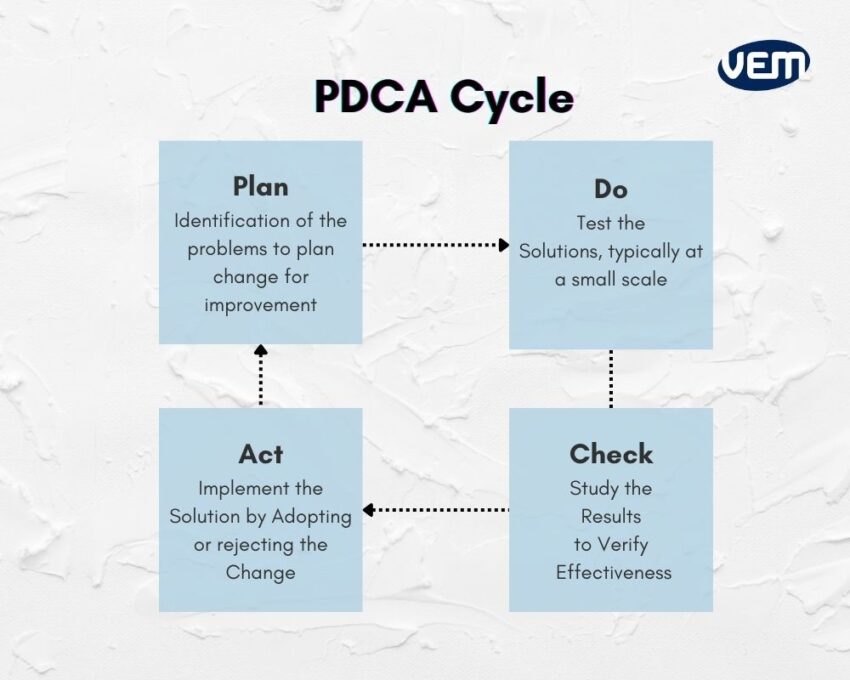
Since processes are continually added, updated, or eliminated, the QMS should be built using a process-based approach. This helps to incorporate a risk-based approach and it can be achieved through the PDCA cycle.
PDCA cycle ensures that all the processes are resourced adequately, and analyzed for improvement opportunities. When your processes are intertwined with such a risk-based approach, it helps to determine the various factors that can cause your processes and QMS to deviate from the expected results. Thus, the PDCA cycle is a preventive measure that helps to mitigate deviations and risks. The diagram below illustrates the PDCA cycle:
The quality management system for medical devices is governed by various international standards and regulations. In this section, we understand two major international markets, i.e. Europe and the United States.
If the medical device manufacturers are marketing and selling in the European region, then they will need to comply with the standards and regulations of ISO 13485:2016, MDR, and IVDR whereas if they are marketing and selling specifically in the US, they will need to comply with the regulations of FDA 21 CFR Part 820 which is also referred to as Quality System Regulations (QSR). Let’s understand the various Standards and Regulations that govern the Medical Device QMS.
ISO, abbreviated for International Organization for Standardization, is responsible for asserting the international regulatory standard ISO 13485 which specifies the QMS requirements. Medical device manufacturers comply with this standard to demonstrate that their medical devices meet the applicable regulatory standards and customer requirements.
ISO 13485 is an internationally agreed set of standards for QMS requirements. It can be used by any manufacturing unit that is involved in the design, manufacturing, and servicing of medical devices. You can read more about ISO 13485 standard here.
ISO 13485:2016 Clause 4.1.6 specifies that medical device manufacturers must document procedures for validating computer software used in the QMS. This should be implemented before the initial use and after any changes to the software.
The Medical Devices Regulation (MDR), also known as EU 2017/745, specifies the various requirements for designing, manufacturing, and distributing medical devices in the European region.
MDR ensures that medical device manufacturers ensure compliance by establishing and maintaining a comprehensive QMS.
In Vitro Diagnostic Medical Devices Regulation (IVDR), also known as EU 2017/746 requires medical device manufacturers to implement a QMS for in vitro diagnostic devices. IVDR ensures compliance and safety principles are specified. It also recognizes compliance with ISO 13485:2016 for QMS requirements.
IVDR poses stringent requirements that emphasize risk-based classification, evaluation of performance, and post-market surveillance.
FDA 21 CFR Part 820 Regulation outlines the requirements of QSR, abbreviated for Quality System Regulation. It specifies the minimum requirements for a medical device QMS to ensure that the medical device is safe and effective for its intended use.
You should note that compliance with FDA 21 CFR Part 820 is mandatory and all medical device manufacturers need to ensure that they are compliant with the 21 CFR Part 820 regulations of FDA if they want to sell their medical devices in the US market.
The 21 CFR Part 820 section 70(i) specifies that medical device manufacturers establish a protocol to validate computer software for its intended use. All the software changes must be validated before approval and all the validation activities along with their results must be documented.
The 21 CFR Part 11 specifies how the electronic records are created, modified, maintained, and stored. It also ensures the accuracy and security of electronic records. In addition, this regulation also sets the guidelines for legally binding electronic signatures.
The FDA 21 CFR Part 820 is similar to the ISO 13485:2016 however there are some major differences between the two regulatory agencies. We have listed these below:
You should note that the QMS supports medical device manufacturers, thus, leading to ISO confirmation and FDA compliance.
EU GMP Annex 11 provides guidelines for GMP i.e. Good Manufacturing Practices for computerized systems. It specifies various requirements to ensure that the computer systems neither reduce product quality nor increase the overall process risk.
There are various regulatory agencies governing the QMS processes for medical devices. In this section, we discuss the requirements and the key obligations of the international standards and regulations.
A quality manual enlists the entire QMS scope. This manual outlines the entire structure of QMS documentation and includes all the processes and procedures of the QMS. A quality manual further includes any non-application clauses that are excluded with justification.
A medical device technical file is a comprehensive technical documentation that consists of various technical documents of the medical device such as
Various documents are involved throughout the product life cycle among various stakeholders such as sponsors, investors, and regulatory agencies.
A medical device QMS must include a system to manage these various documents and this process is referred to as document control.
Today, there are various automated quality management software that feature robust document control capabilities. These software solutions collect data, route documents for review and approval processes, and store them in a central location.
Various international regulations such as the FDA 21 CFR 820 and ISO 13485:2016 require that medical device manufacturers offer specific training to their employees. This particularly means that all the training procedures and processes are constantly evaluated. In addition, all employee training records must be maintained.
If there is any change in the manufacturing process, it must be learned by all the involved employees. Thus, a training management system must be incorporated to ensure streamlining of the entire training process. This system must include and cover various aspects of training management such as assigning training tasks to specific employees, distributing the required training material, tracking all the activities, and measuring the effectiveness of the training through evaluations.
An audit management process is necessary to ensure that the quality management system is compliant. Various regulations such as the FDA 21 CFR 820 and ISO 13485:2016 require manufacturers to establish an audit process and conduct regular quality audits. An established audit management system must schedule activities and send notifications to the right personnel.
It is imperative to include a resource management system that helps the company to identify and allocate necessary resources that are required to manufacture the medical device.
In this system, it is required that the medical device manufacturers ensure and develop the competency of qualified personnel through training procedures. This system is also further applicable to overall infrastructure, software that supports business operations, processes, workspaces, and overall work environment.
You should note that failure to comply can lead to significant regulatory violations.
Various regulatory agencies require medical device manufacturers to document procedures for management review. This is a crucial system and to verify the sufficiency, and effectiveness of the system, the top management is required to examine the QMS at pre-planned intervals.
Customer-related processes cover the regulatory requirements of the patient or the end-user of the medical device. These processes include systems for distributors, purchasing organizations, and logistics resources.
CAPA, abbreviated for corrective actions and preventive actions, is a requirement of several regulatory bodies.
The primary goal of the CAPA process is to prevent and/or resolve various issues that can impact product quality. These issues can range from nonconformances, to audit findings and complaints. In this process, all actions must be documented and resolved on time.
CAPA standardizes responses for corrective actions that need to be taken. It includes collecting information or data, further identifying and investigating the issue, and ultimately implementing corrective and preventive action.
The below diagram illustrates the key CAPA processes:
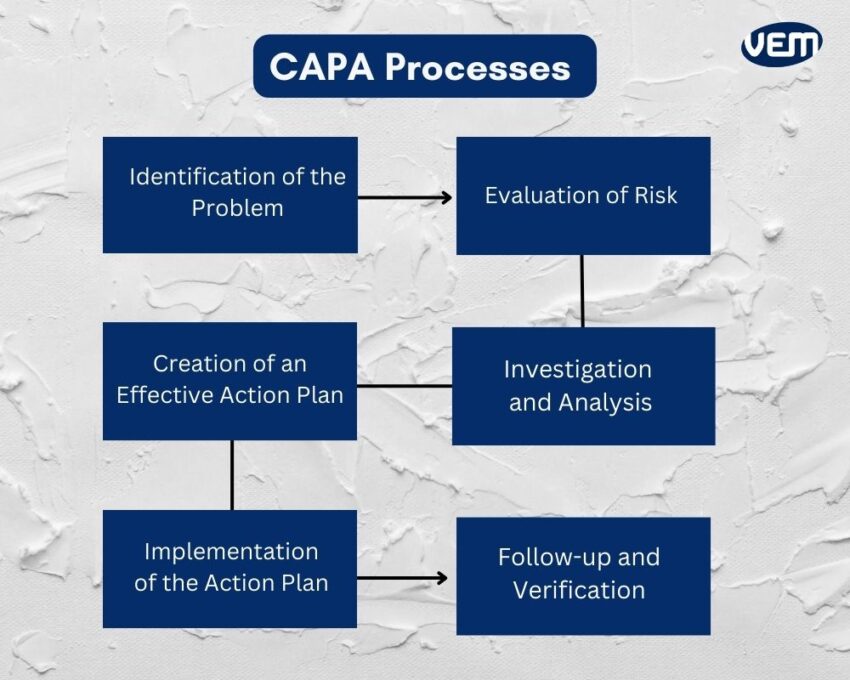
In addition, CAPA also encompasses communicating with the concerned and appropriate personnel and enabling information for review.
Medical device quality management system is a key regulatory requirement for medical device manufacturers however; it can seem daunting to establish a quality management system. If you are looking for a QMS solution that can streamline your quality management processes, you can contact us and talk to our experts.
At VEM-Tooling, we have a team of expert engineers who have a vast experience of over 20 years in manufacturing high-quality medical device plastic parts. We can help you build a QMS from the start or assist you with QMS implementation as well.